On This Page
Overview
Fungal Diseases refer to a group of discomforts caused by a fungal infection. Nearly 200 million people have serious fungal diseases, which cause a major impact on their health or life. Due to a lack of clinical approaches and diagnostic test performances, many fungal diseases are not even properly recognized. It is very important for everyone to have a general awareness of fungal infections and their complications. Mycosis the medical term for a fungal invasion in human beings. The fungal disease may limit to the skin only or spread into tissues, bone, and organs or affects the whole body. Moisture is a favorable condition for fungus to hibernate. Usually, skin folds and moist areas of the body like toes, genital area, underarms, and under the breasts are the more prone sites of infection.
So, Your search related to herbal remedies for fungal diseases, natural treatment for fungal diseases, herbal remedies for fungal infection, natural treatment for fungal infection, alternative treatment for fungal infection, and alternative treatment for fungal diseases end here. Consult with Dr. Sahil Gupta (B.A.M.S., M.H.A.) and follow his guideline, you will be fine soon.
Causes of Fungal Infection
Fungus is one of the wide ranges of living organisms that live in varied habitats like on soil, on plants, household surfaces even on body skin. Among 1.5 million different species of fungi, only about 300 are harmful to human health. Some of them are beneficial to humans like mushrooms, baker’s yeast, and some medicines. Fungal infections can be primary in those who are relatively healthy and can be opportunistic such as in a person with a weak immune system. People living in damp places like coastal regions where a higher concentration of mold is present are at more risk. Some other susceptible conditions are:
- Chronic illnesses like Diabetes, Cancer, AIDS, etc.
- Obese person
- Patients taking antibiotics and corticosteroids from long duration
- Weakened immune system
In Ayurveda, a variety of reasons are explained as the cause of fungal infection. It includes improper food, inappropriate regimen, and lifestyle, mental stress and tension, unhygienic practices, etc.
Classification of Fungal Infection
Fungal infections can be either localized or systemic. The infections aggressively spread from one side to the other and sometimes can even be fatal. A few types of fungal infections are listed below which are common in humans.
A. Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is caused by a type of fungus called Aspergillus. Its habitats in stored grain, dead leaves, decaying vegetation, and compost pits. Aspergillosis is a type of opportunistic fungal infection that occurs in people who are suffering from health issues like allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, or asthma for a long duration or those having weakened immune systems. Also, it easily affects immune-compromised patients having HIV or AIDS, Cancer, Lung Abscess, Tuberculosis, and Cystic fibrosis. On the basis of localization of Aspergillus fungus following are the types of Aspergillosis:
- Aspergillosis Sinusitis
- Broncho-pulmonary Aspergillosis
- Cutaneous (skin) Aspergillosis
- Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis
In Ayurveda, the condition called Tamaka Swasa is related to Broncho-pulmonary Aspergillosis. The aggravating factors of Tamaka Swasa as per Ayurveda include cloudy climate, exposure to water, cold weather, wind, etc. The main symptoms of Tamaka swasa are stiffness of the head and neck, cough, hoarseness of voice, tastelessness, runny nose, thirst, increased rate of respiration, sweating, etc.
Ayurvedic Reference of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis

B. Candidiasis
Candidiasis is the most common type of fungal infection caused by the yeast Candida albicans. Candida yeast usually resides on the skin, the mucous membrane of the mouth, vagina, and the digestive tract with no potential harm. But overgrowth of these microorganisms in favorable environments results in Candidiasis (a type of yeast infection). Candida Yeast overgrows in:
- Hot and Humid conditions
- Poor hygiene
- Sites of diaper rashes
- Tight, synthetic undergarments
- Obesity
- Psoriasis and eczematous skin lesions
- Weakened immune system
On the basis of body part affected, following are the types of Candida Yeast infection:
- Oropharyngeal Candidiasis (Thrush)
- Genital Candidiasis (Penile and Vulvo-vaginal Candidiasis)
- Diaper Rash or skin candidiasis
- Invasive Candidiasis or Candidemia
- Angular Cheilitis
- Nail Candidiasis
- Chronic muco-cutaneous Candidiasis
In Ayurveda, symptoms similar to Candida infection in different sites are explained. Symptoms of oropharyngeal candidiasis are similar to that of Mukhapaka (Mouth ulcer) caused by vitiation of Kapha dosha. It is mainly manifested as itchy mouth ulcers with sticky discharge, the sweetness of the mouth, etc.
Ayurvedic References of Candida Yeast Infection

C. Dermatophytosis (Tinea)
Dermatophytosis includes fungal infections of the skin and nails caused by molds. Tinea is the Latin term meaning Fungal Infection. Dermatophyte infections are also called ringworm or Tinea. Tinea infections are very common, and it affects any age group. Tinea results in circular ring-type red patches on the skin, nails, hair, and feet. Molds are a type of fungi that need keratin protein for their growth. Human skin, hair, and nails are structured from keratin proteins. That’s the reason why Dermatophytes live here. Dermatophytosis in humans is caused by Epidermophyton, Microsporum, Trichophyton, etc.
Signs and Symptoms of Tinea Infection
- Irritation
- Scaly Skin
- Redness
- Itching
- Swelling
- Blisters
Methods of Transmission of Tinea Infection
- Human to Human: Direct skin to skin contact
- Object to Human: Using clothing, towels, bed linens, comb, etc. of the infected person
- Animal to Human: Via Pet Animals
Classification of Tinea
Dermatophytes infect the skin and according to site of infection classification is as follows.
- Tinea Capitis (Ringworm of the Scalp)
- Tinea Pedis (Athletes Foot)
- Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch)
- Tinea Unguium (Nail Fungus)
- Tinea Barbae (Beard Infection)
- Tinea Versicolor
- Tinea Manuum
Tinea Capitis (Ringworm of the Scalp)
Tinea Capitis develops inside the hair follicles on the scalp. The fungi attack the outer layer of the scalp and hair shaft. Ring-like circular rashes will appear on the scalp skin.
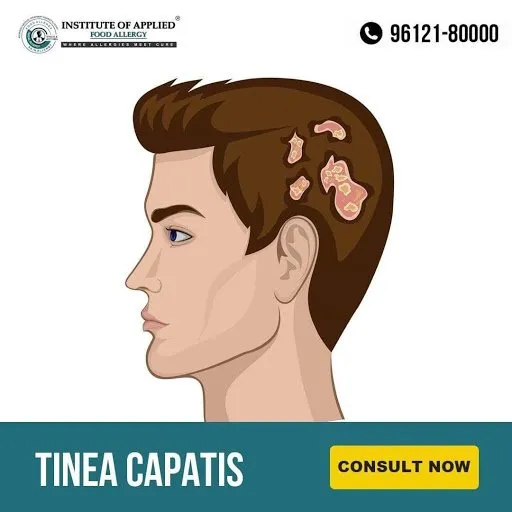

Ayurvedic Reference of Tinea Capitis (Arumshika)

Symptoms of Tinea Capitis (Ringworm)
- Red scaly, Itchy patch
- Ring-shaped Patch
- Flaky
- Tender and Sore to Touch
- Pus filled bumps on the Scalp
- Bald patches on the Scalp
Prevention of Tinea Capitis (Ringworm)
- Keep body clean
- Wash hands frequently
- Don’t share personal items with others
- Keep the skin dry
- Wash bedding regularly.
- Shampoo regularly
- Replace or disinfect hair tools regularly.
Differential Diagnosis of Tinea Capitis
- Alopecia Areata
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Drug Eruptions
- Impetigo
- Plaque Psoriasis
- Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Eczema
In Ayurveda, a condition similar to Tinea capitis is mentioned as Arumshika. It is the condition caused by vitiation of Pitta dosha, Kapha dosha, Rakta, and also by the attack of micro-organisms.
Tinea Pedis (Athlete’s Foot)
It is a fungus infection that usually grows in between the toes. Often occurs in people whose feet have become always sweaty with tight-fitting shoes. It spreads very easily.
The Moccasin variety of Athlete’s Foot causes chronic dryness and scaling of soles that extend up to the side of the foot. It can affect both feet and can spread to the hands if there is a scratch or prick at the infected parts of the feet. It can be mistaken for eczema or dry skin.
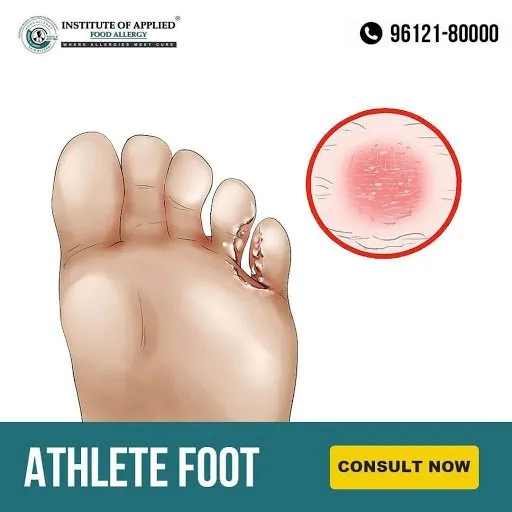
Ayurvedic Reference of Tinea Pedis (Alasa)

Signs and Symptoms of Tinea Pedis (Athletes Foot)
- Stinging
- Burning
- Blisters
- Ulcers
- Scaly rash (Especially in between 4 & 5th toes)
Triggering Factors of Tinea Pedis
- Warm humid conditions
- By contact with infected person or surfaces
- Excessive sweating
- Consumption of immune-suppressive medications
- Poor peripheral circulation
- Infection can spread through hands, nails (can also infect toenails), groin area (jock itch is caused by the same fungus)
- Damp socks, shoes
Prevention of Tinea Pedis
- Keep feet dry, especially in between the toes.
- Change socks regularly.
- Keep personal shoes and socks.
- Protect feet from public places.
- Don’t share socks, shoes, and belongings.
- Avoid wearing footwear for long periods.
Differential Diagnosis of Tinea Pedis
- Foot Eczema
- Contact Allergic Dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Plantar Pustulosis
- Plantar Keratoderma.
Tinea pedis is explained in Ayurveda as the condition called Alasa. It is said to occur due to certain worm infestation or microbial attacks.
Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch)
It’s a Fungal Infection in the skin of the genitals, inner thighs, and buttocks. It causes an itchy, red ring-shaped rash on the warm and moist area of the body often affecting the inner thighs and the groin area. It is common in athletes, in people with excess perspiration, overweight persons, etc.
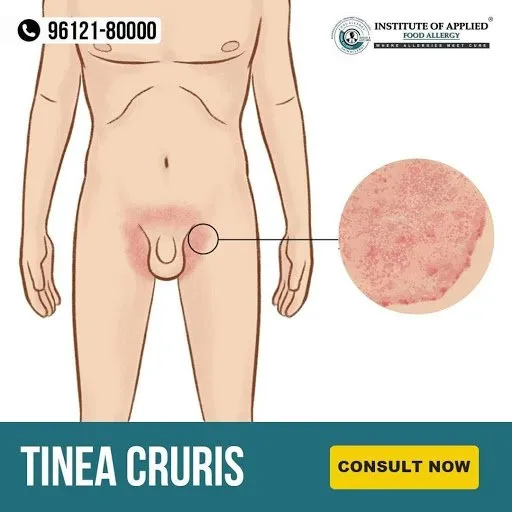
Ayurvedic Reference of Tinea Cruris (Pama)

Signs and Symptoms of Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch)
- Reddish Skin Rash
- Itching
- Burning
- Flaky, Scaly Skin
- Ring-shaped rash bordered with a line of small blisters
Spread of Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch)
- From person to person
- By sharing belongings like towels, clothing, etc.
- Spreads from feet to groin through hands or towel.
Risk Factors for Tinea Cruris
- Tight Underwear
- Overweight
- Excessive sweating
- Weakened Immune System
- Diabetes
Prevention of Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch)
- Stay Dry
- Wear Clean Clothes
- Treat Athlete’s Foot (if any)
- Don’t share belongings
Jock Itch can be related to Pama explained in Ayurveda. It is caused by the vitiation of Kapha and Pitta dosha.
Tinea Unguium (Nail Fungus)
It is a fungal infection causing nail brittle, crumbly, and thickened. It is caused by trichophyton rubrum and tinea interdigitale. Fungus may affect one or more toenails. Nail fungus is often confused with non-infected nail dystrophy particularly psoriasis, dermatitis, lichen planus, viral warts, aging changes, etc.
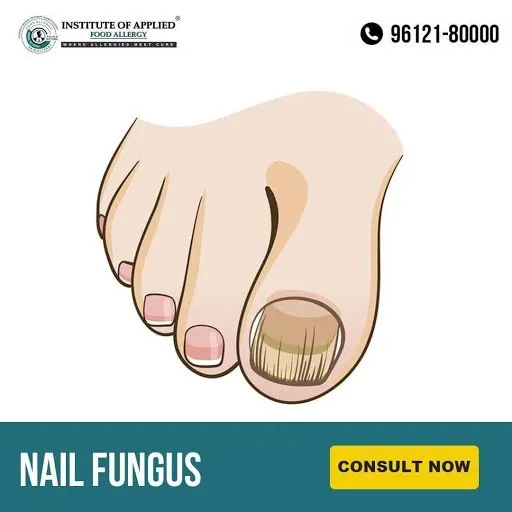
Ayurvedic Reference of Tinea Ungium – Kunakha

Patterns of Nail Fungus
- Lateral Onychomycosis – White, yellow opaque streak appears at one side of the nail.
- Subungual Hyperkeratosis – Scaling occurs under the nail.
- Distal Onycholysis – End of the nail lifts up, free edge often crumbles.
- Superficial White Onychomycosis – Flaky white patches & pits appear on top of the nail plate.
- Proximal Onychomycosis – Yellow spots appear in half moon.
- Complete destruction of nails.
Signs and Symptoms of Nail Fungus (Tinea Unguium)
Nail becomes,
- Thickened
- Whitish to Yellow-brown discolored
- Distorted in shape
- Brittle, Crumbly or Ragged
- Dark Color
- Slightly foul-smelling
Risk Factors of Nail Fungus
- Heavy sweating
- History of Athlete’s Foot,
- Walking barefoot,
- Nail Injury
- Psoriasis
- Diabetes
- Weakened Immune System
Complications in Nail Fungus
- In severe cases, it may cause permanent damage to the nails. It may lead to other serious infections.
- A diabetic person is at greater risk.
- In the suppressed immune system.
Prevention of Nail Fungus
- Trim nails
- Wash and moisturize nails regularly
- Change socks regularly
- Use sterilized nail tools.
- Disinfect shoes
In Ayurveda, a condition similar to Nail Fungus is explained as Kunakha. It is said to be caused by trauma.
Tinea Barbae
Tinea Barbae is also known as Tinea Sycosis or Barber’s Itch. It is a fungal infection of the skin, hair, hair follicles of the beard area. It is most common in men, it may also affect women who have dark, coarse hair on the face or neck. It is mostly seen in adult males and older teens. The most common locations of Tinea Barbae are the chin, cheeks, neck, and upper lips.
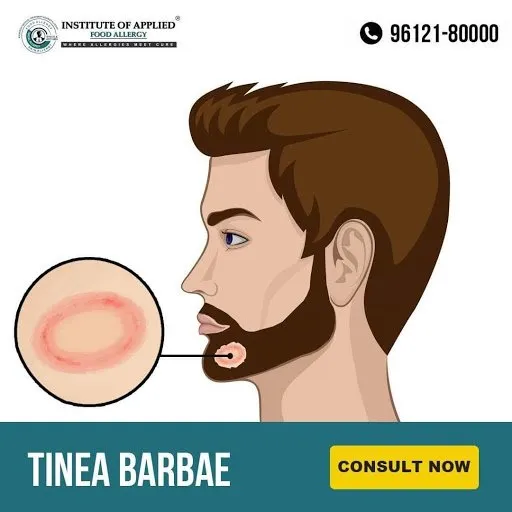
Ayurvedic Reference of Tinea Barbae – Indraluptha – Rujya

Signs and Symptoms of Tinea Barbae
- Red Scaly patch
- Small pus-filled bumps (Pustules)
- Itching
- Swelling
- Hair can be pulled out easily
- Fever
Causes of Tinea Barbae
- Warm, humid climate,
- Can spread from animals to humans,
- So agricultural workers are most infected due to direct contact with an infected animal.
- From cattle (Tinea Verrucous)
- From horses (Tinea Mentagrophytes)
Prevention of Tinea Barbae
- Examine all animals for fungal infection and treat them accordingly by a veterinary doctor.
In Ayurveda, Tinea barbae is explained as Indraluptha. It is a condition affecting hair follicles. It is also called Rujya or Chacha.
Tinea Versicolor or Pityriasis Versicolor
It is a fungal infection caused by the fungus Malassezia furfur (a type of yeast) found on the surface of the skin that causes small discolored patches. Tan, brown, salmon or white scaly patches appear on the trunk, neck, and abdomen and occasionally on the face in a typical pattern. Small patches may join to form larger patches. Dark skin people have lighter patches, but fair skin may get darker or lighter patches. It is most common in younger adults and is not contagious. Yeast like Malassezia usually live in large communities on the skin to protect from other infections. They live alongside the body’s cells in symbiotic relationships with skin cells and tiny organisms supporting and benefiting each other. Sometimes this yeast can grow out of control due to a weakened Immune System thus causing chronic relapsing Tinea Versicolor.
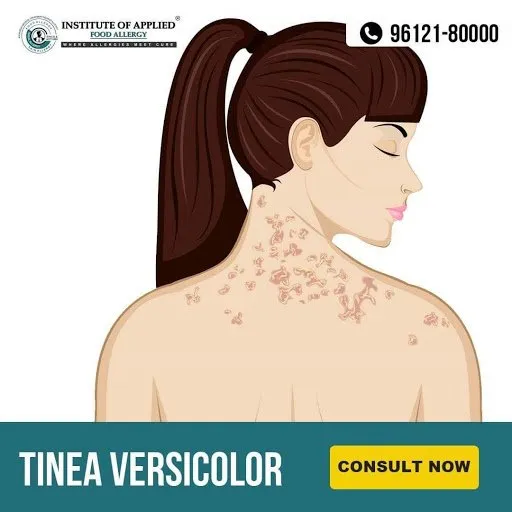
Ayurvedic Reference of Tinea Versicolor – Rikshajihva

Signs and Symptoms of Tinea Versicolor
- Mild Itching
- Scaling patches
- Light or Dark Skin Discoloration
Causative Factors of Tinea Versicolor
- Hot, humid weather
- Excessive sweating
- Oily skin
- Hormonal changes
- Weakened immunity
Prevention of Tinea Versicolor
- Don’t wear Tight Clothing
- Reduce Exposure to Sun
- Avoid using Oily Skin Products
Differential Diagnosis in Tinea Versicolor
- Rash caused by Pityriasis rosea is similar to Tinea versicolor.
- Some conditions with symptoms such as Vitiligo are often mistaken for Tinea versicolor.
Tinea versicolor can be related to Rikshajihva in Ayurveda. It is caused by the vitiation of Vata dosha and Pitta dosha.
Tinea Manuum
It is a Fungal Infection of the hands. It is also called Ringworm and is contagious. Manuum means the infection is on one or both hands. Red scaly rash that usually has a border that is slightly raised, creates a Ring so referred as Ringworm.
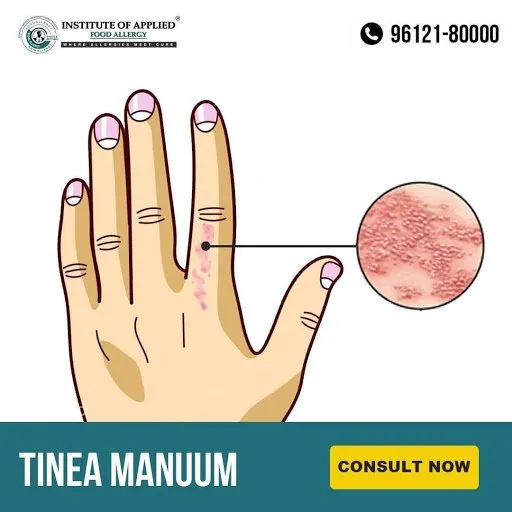
Ayurvedic Reference of Tinea Manuum – Dadru

Signs and Symptoms of Tinea Manuum
- Itching
- Dryness
- Scaly
- Burning
- May Peel and Flake
Risk Factors of Tinea Manuum
- Using Public Showers
- Excessive Sweating
- Tight Fitting Clothing
- Human to Human
- Animals to Human
- From Hedgehog – Trichophyton Erinace
- Cattle – T. Verrucosum
- Cat / Dog – Microsporum Canis
- From Soil – Mannizzia Gypsea
Prevention of Tinea Manuum
- Keep Hands Clean and Dry
- Avoid contact with an active case of Tinea
- Wear disposable gloves when treating Infected Skin.
- Tinea Manuum is often confused with Hand Dermatitis
In Ayurveda, the condition of Tinea Manuum is described as Dadru. It is caused by the vitiation of Kapha dosha and Pitta dosha.

“Fungal infections are very common yet distressing diseases affecting many of the people around us. Dr. Gupta’s IAFA® is a trustworthy institution for the complete cure of your ailments caused by fungal infections. Institute of Applied Food Allergy® follows genuine Ayurveda to ensure you a healthy living”.
IAFA® welcomes you to a healthy and happy life through Ayurveda!!
Ayurvedic Allergy Specialist
CEO & Founder of IAFA®
At last, Easier Fungal Infection Management

Trusted by
More than 90,000 Patients

Convenient
at-Home Treatments

9.2 / 10
Customer Satisfaction Score
Ayurvedic Treatment for Fungal Infection
Ayurveda incorporates internal as well as external medicines for the treatment of Fungal Infection. The unique Ayurvedic treatment protocol ensures a complete treatment for various skin infections.
Internal Medicines
Following medicines can be advised based on type and site of infection:-
- Panchatiktam Kwatham
- Patoladi Kwatha
- Patolamooladi Kwatha
- Nimbadi Kwatha
- Kaisora Guggulu Tablet
- Vilwadi Tablet
- Dooshivishari Tablet
- Manibhadra Gula
- Avipathi Churna
- Triphala Churna
- Khadirarishta
- Patolasava
- Nimbamruthasava
External Medicines
External medicines as listed below can be provided based on stage and site of infection:-
- Triphala Churna
- Nimbadi Churna
- Nalpamaradi Churna
- Aragwadhadi Kwatha
- Guduchyadi Kwatha
- Tuthadi Tablet
- Rasothamadi Lepa
- Dhanyamla
- Dineshavalyadi Kera
- Vitpala Kera
External Therapies
Following procedures help in easy healing of wounds and ulcers:-
- Swedana (Sweating therapy)
- Padaavagaha (Foot bath)
- Lepa (Medicinal paste)
- Abhyanga (Oil massage)
- Kshalana (Washing)
Purification Therapies in Fungal Infection
- Virechana (Purgation)
- Vamana (Emesis)
- Raktamokshana (Blood-letting)
Single Herbs in Fungal Infection
Use of following single herbs can be suggested in different forms as per condition of patient and infection.
- Nimba (Azadirachta indica)
- Patola (Trichosanthes dioica)
- Tila (Sesamum indicum)
- Pippali (Piper longum)
- Haritaki (Terminalia chebula)
- Shatavari (Asparagus racemosus)
- Haridra (Curcuma longa)
- Kushta (Saussurea lappa)
- Chitraka (Plumbago zeylanica)
- Amalaki (Emblica officinalis)
Diet Management in Fungal Infection
Pathya (Do’s)
- Consume old harvested grains and cereals
- Include more fruits and vegetables in the diet
- Drink warm water
- Take easily digestible food
- Have warm and fresh food always
- Drink adequate water
- Green gram
- Pomegranate
- Gooseberry
- Take food only after digestion of the previous meal
- Mild to moderate exercise
- Use of separate personal items
- Maintain personal, social, and environmental hygiene
- Use chappals when walking through mud, dust, or dirty water
- Wear loose and dry garments
- Change clothes, bedsheets, etc. at regular intervals
- Expose to mild sunlight daily in morning and evening
- Sleep approximately for 7 hours per day
- Positive and stress-free mind
- Maintain healthy and happy relation between friends and relatives
Apathya (Don’ts)
- Excessive sweet, salty, spicy, and sour food
- Fermented food
- Heavy to digest food
- Non-vegetarian diet
- Curd
- Pappad
- Black gram
- Old and refrigerated food
- Reheated food
- Taking food before digesting the previous meal
- Day sleep
- Lack of exercise
- Lack of enough sleep
- Stress and mental tension
- Lack of personal hygiene
- Exchange of personal items
- Tight and unclean garments
- Keeping body parts like folds, genitals, etc. wet and moist.
Yoga and Pranayama in Fungal Infections
Various yoga postures help to make the mind and body relaxed. This reduces the intensity and recurrence of various skin diseases including fungal infection. It helps to increase blood circulation and rejuvenates body cells. Following postures will be especially beneficial in fungal infections:
- Surya namaskar
- Supta Baddha Konasana
- Marichyasana
- Padmasana
- Sukhasana
- Sarvangasana
- Savasana
- Vajrasana
- Paschimottanasana
Pranayama helps to attain relaxation in the mind. It promotes the healing of ulcers and wounds. Pranayama ensures blood flow to all body parts. It confirms oxygen supply and helps the formation of new cells.

Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What is Aspergillosis?
Answer: Aspergillosis is an infection caused by the fungus Aspergillus that affects the respiratory system and manifested as sinusitis, cough, dyspnea, etc.
Question: What are the Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot?
Answer: Manifestations of Athlete’s Foot include scaly rash, itching, burning, blisters, ulcers, etc.
Question: How Ayurveda helps in the Management of Fungal Infections?
Answer: Ayurveda combines internal and external medicines and therapies for the effective and complete cure of various fungal infections. Fungi may affect different body parts and cause varied symptoms and manifestations. Ayurveda suggests a unique treatment for each type of infection.
Question: What are the Risk Factors of Jock Itch?
Answer: People wearing tight undergarments, who are overweight, sweat easily, have diabetes, etc. are more prone to have Jock Itch.
Question: How can Nail Fungus be Prevented?
Answer: Nail fungus can be prevented by trimming nails, changing socks regularly, keeping the foot and nails dry and clean, disinfecting shoes, etc.
Question: How Ayurveda helps in the management of Fungal infections?
Answer: Ayurveda combines internal and external medicines and therapies for the effective and complete cure of various fungal infections. Fungi may affect different body parts and cause varied symptoms and manifestations. Ayurveda suggests unique treatment for each type of infection.
References
- Ayurvedic Aspects of Allergies and Fungal Infections, Edition 2021, by Sahil Gupta, Fungal Diseases Chapter No. 41, Page No. 245-266.
- Sushruta Acharaya, Sushruta Samhita edited with Ayurved tattva sandipika, Uttartantra, editor Kaviraja Ambika Dutta Shastri, Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, Varanasi, Reprint 2017.
- Charak Acharya, Charak Samhita edited with Vidyotni commentary, Sutra Sthana, Nidan Sthana & Chikitsa Sthana, editor Pt. Kasinatha Shastri & Dr. Gorakha Natha Chaturvedi, Chaukhambha Bharati Academy, Varanasi, Reprint 2018.
- Sharma PV, Sharma P. Charaka Samhita: Vimanasthanam. 23rd ed. Ch 5. Varanasi, India: Chaukhambha Orientalia; 1981. p. 226-40.
- Chakravorty RC. Head and neck diseases in an ancient Indian surgical text (The Sushrut Samhita) Med Hist. 1971; 15:393-6.
- Athavale VB. Dant rogas. In: Athavale VB, editor. Dentistry in Ayurveda. 1st ed. New Delhi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Pratishthan; 1999. p. 7-11.
- Vaidya Harisastri Parodkar, Ashtanga Hridaya A compendium of Ayurvedic system, with commentaries of Arunadatta and Hemadri, Bombay, Nirnayasagar Press, 1989, p 785-786.
- Vaidya, LC. Ashtanga Hridayam with Sarvangasundari Vyakhya, Varanasi, Motilal Banarasidas, 1963, p 596.
- Narayan Ram A, Yadavji Trikamji A. Sushruta Samhita, Bombay, Nirnayasagar Press, 1945, p 324.
- Sharma P, editor. Sutrasthana, Chapter 20, verse 11. In: Charak Samhita of Acharya Charak. Vol. I. 8th ed. Varanasi, India: Chaukhambha Orientalia; 2007. p. 139.
- Tripathi B. Charak Samhita with Hindi commentary ‘Charak Chandrika’, Chapter 5, citation no. 204. Varanasi, India: Chaukhambha Prakashan. p. 186.
- Gupta Atrideva, Astangahrdaya, Chaukhambha Prakashan Varanasi, edition reprint, 2007, Nidana Sthan 14/24, p. 273.
- Trikamji Yadavji Acharaya, Agniveshakrita Charak Samhita, Chakarpani Commentary, Chikitsasthan, Chapter 7, Kustha Chikitsa, verse no. 23, Varanasi, Chaukhambha Surbharti Prakashan, p. 451, Reprint 2011.
- Shastri Ambika Dutt commentary on Sushrut Samhita, Sutra Sthana, Chapter 33, Avarniya, verse no. 4, Varanasi, Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan p. 156, Reprint 2007.
- Srivastava Shailja, Sharaghdhara Samhita, Madhyam khanda Chapter 7, Vataka Kalpana, verse no. 71-80, Chaukhambha Orientalia, p.204, Reprint 2009.
Was this Page Helpful?
So IAFA® Root-Cause Treatment of Your Fungal Diseases is Just 3 Steps Away!

01. Connect With Us
Share your history of illness or Book your appointment

02. Consult With Us
Dr. Gupta a certified Ayurvedic Allergist Consultant

03. Root Cause Treatment
Get an accurate diagnosis, medicines, diet & lifestyle change
Real Case Studies – Successfully Treated Patients
Real Case Studies of Successfully Treated Patients from All Around the World by IAFA Ayurveda®

9 Year Old Female Patient Recovered from Chronic Allergic Bronchitis – A Case Study
This case study presents a 9-year-old female patient who has successfully recovered…

12-Year-Old Child Recovered from Sun Allergy and Polymorphous Light Eruption (PMLE) – A Case Study
This is a case study of a 12-year-old child who has successfully…

40-Year-Old Female Patient Recovered from Dyshidrotic Eczema and Onychomycosis – A Case Study
This case study highlights the successful recovery of a 40-year-old female patient…

40-Year-Old Female Patient Recovered from Urticaria and Angioedema – A Case Study
This case study focuses on a 40-year-old female patient who has successfully…
Read More Articles

Mast Cell Diseases
Discover Ayurvedic treatment for Mast Cell Diseases, including types, causes, symptoms, and…

High Immunoglobulin-E (IgE) Levels
Discover Ayurvedic treatment for high Immunoglobulin-E (IgE) levels. Learn about the causes,…

Histamine Intolerance
Discover Ayurvedic treatment for histamine intolerance, its causes, symptoms, and natural treatment.…