On This Page
Introduction
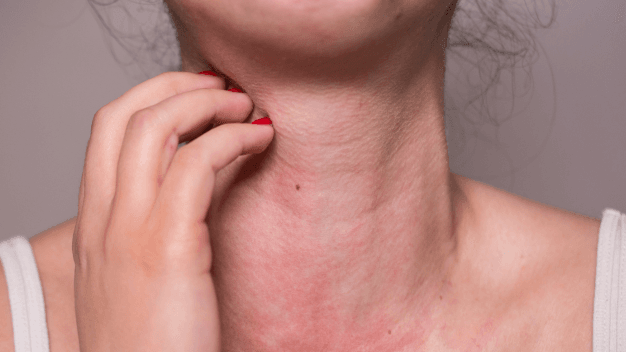
Are you suffering from unexplained allergies, recurrent anaphylaxis, or skin rashes? Do you frequently experience swelling, itching, or sudden allergic reactions? Are abdominal pain, dizziness, or flushing disrupting your daily life?
If so, you might be dealing with Mast Cell Diseases, where excessive histamine is released by immune cells causing widespread inflammation in the body.
Conditions like Mastocytosis and Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS) result in allergic and inflammatory symptoms affecting the various parts of our body like the skin, respiratory system, and gastrointestinal system, and even affect cardiovascular health. As such no diseases are co-related with mast cell diseases but as per the symptoms manifest in mast cell diseases can be correlated with disorders with Pitta-Vata imbalance, blood toxicity (Rakta Dushti), and toxins (Ama), which leads to hypersensitivity reactions similar to urticaria (Sheeta Pita, Udarda) and bleeding disorders (Rakta Pitta), etc.
Ayurvedic treatment for Mast Cell Disease includes detoxification therapies like purgation therapy (Virechana) and bloodletting therapy (Rakta Mokshana), along with the use of potent herbs like Guduchi, Haridra, Neem, and Shirish, etc. which stabilize the mast cells in the body and modulate immunity. A well-balanced personalized diet combined with stress management through Yoga, Pranayama, and meditation, also helps in regulating immune responses.
If you are suffering from the above-mentioned diseases then don’t worry – Dr. Sahil Gupta and the expert team at IAFA Ayurveda provide an Ayurvedic approach to managing mast cell diseases by addressing the root cause rather than just symptoms, helping restore the balance of the Dosha, strengthen immunity (Vyadhi Kshmatva), and bring lasting relief. Reclaim your health naturally with IAFA Ayurveda!
What is Mast Cell?
Specialized immune cells that play an important role in the body’s defense system are known as mast cells. It originates in the bone marrow like all other blood cells. These cells are found in connective tissues, especially near blood vessels, nerves, and mucosal surfaces, such as the lungs, skin intestines, etc. These mast cells contain granules filled with cytokines, histamine, and other inflammatory mediators, which are released in response to infections, allergens, or injuries in the body.
What is the Role of Mast Cells in the Body?
As mentioned above, Mast cells are essential for immune defense, wound healing, and maintaining homeostasis. Their primary function of mast cells included triggering reactions by releasing histamine, as allergen comes in contact with the body leading to various symptoms like swelling, inflammation, itching, etc.
Mast cells also release cytokines that help to fight against infection and recruit other immune cells. Along with this mast cells help in modulating inflammatory response, wound healing influence pain perception, etc.
What are Mast Cell Diseases?
The group of disorders characterized by abnormal growth, accumulation, or overactivation of mast cells, which leads to excessive release of inflammatory mediators like cytokines, histamines, prostaglandins, etc. in the body is known as mast cell diseases.
Mast cell diseases include Mastocytosis, a condition where mast cells multiply excessively in various organs, and MCAS (Mast Cell Activation Syndrome), where mast cells release without an increase in their number of excessive mediators.
Although mast cell diseases are mainly identified in the skin, gastrointestinal disturbances, respiratory issues, cardiopulmonary, neurological symptoms, and anaphylaxis may be seen. Mast cell diseases can be triggered by infections, stress, allergens, temperature changes, and even certain foods or medications can trigger mast cell diseases.
What are Mast Cell Diseases – As Per Ayurveda?
Mast cell diseases are not directly mentioned in Ayurveda but explain similar pathophysiology (Samprapti) involving Pitta-Vata vitiation, blood vitiation (Rakta Dushti), microchannel obstruction (Stroto Rodha), toxins accumulation (Ama Uttapati), etc. Various diseases like urticaria (Sheeta Pitta, Udarda), bleeding disorders (Rakta Pitta), erysipelas (Visarpa), skin diseases (Kustha), and gut disorders like Grahni share clinical similarities with mast cell disorders.
The excessive histamine response seen in the pathology of the mast cell diseases aligns with excess heat and inflammation i.e. Pitta Aggravation as per Ayurveda, while sudden hypersensitivity reactions resemble irregularity and overreactivity i.e. Vata disturbances. Accumulated toxins (Ama) and vitiated blood (Rakta Dushti) contribute to chronic (Jeerna) inflammation, leading to systemic mast cell dysfunction.
Who Gets Affected by Mast Cell Diseases?
This disease affects individuals of all ages, genders, or ethnicities, but certain factors may increase susceptibility to mast cell diseases. A condition where mast cells multiply abnormally i.e. Mastocytosis, is often linked to KIT gene mutations and appears in childhood or adulthood whereas a condition where mast cells release excessive inflammatory mediators i.e. Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS), is more common in adults but can also affect children.
Along with this, people with a history of asthma, autoimmune diseases, various allergies, chronic inflammation, or frequent anaphylactic reactions are at higher risk of having mast cell diseases. Conditions like Irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, CFS, and POTS are often found with mast cell dysfunction. Environmental triggers like pollution, stress, infections, certain foods (high histamine or processed foods), and temperature changes can also contribute.
How Common are the Mast Cell Diseases?
As per the recent survey, mast cell disease is considered rare in Mastocytosis having a prevalence of approximately 13 in 100,000, and MCAS has prevalence approximately from 1 in 6 people to less than 1 in 1000. In the United States, studies done on 2018, showed that the incidence of mastocytosis was found to be 0.046 per 10,000 among the general population. A study in The Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology reported that the overall prevalence of idiopathic mast cell activation syndrome is 4.4%.
Types of Mast Cell Diseases
Mast cell diseases can be classified into three main types:-
- Mastocytosis
- Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS)
- Other Mast Cell-Related Disorders
1. Mastocytosis
The condition in which there is excessive proliferation and accumulation of mast cells occurs. It is classified into two types one that only affects the skin i.e. cutaneous and one that affects multiple organs i.e. systemic.
1.1) Cutaneous Mastocytosis – Cutaneous Mastocytosis is mainly seen in children. This type of mast cell only affects the skin and they have no effect on internal organs. It is further divided into three types:-
1.1.1) Urticaria Pigmentosa / Maculopapular Cutaneous Mastocytosis (MPCM): The most common type of cutaneous Mastocytosis which is characterized by brown-red papules or macules that show Darier’s sign means urticate when stroked. It is mainly seen in infants and resolved when adolescence is attained.
1.1.2) Diffuse Cutaneous Mastocytosis (DCM): This is a rare type of cutaneous Mastocytosis, but it is a very severe condition in which skin thickens and blister formation occurs as a result of widespread mast cell infiltration. In very severe cases it may result in hypotension and anaphylaxis.
1.1.3) Solitary Mastocytoma: This type of Mastocytosis is often resolved spontaneously in childhood. In this type, single or few localized nodules of mast cells are formed.
1.2) Systemic Mastocytosis (SM) – Mastocytosis affects the internal organs like the liver, spleen, bone marrow, etc. as it involves mast cell infiltration of internal organs. Based on severity it is further divided into 5 types:-
1.2.1) Indolent Systemic Mastocytosis (ISM): This is the mildest form of systemic macrocytosis with slow progression in which symptoms like itching, flushing, and gastrointestinal discomfort occur. This type of bone marrow is involved but without major organ dysfunction.
1.2.2) Smoldering Systemic Mastocytosis (SSM): This type of systemic Mastocytosis shows intermediate severity with more mast cell burden than indolent systemic mastocytosis. With time this type may progress to an aggressive form.
1.2.3) Aggressive Systemic mastocytosis (ASM): In this type of systemic mastocytosis organ damage like bone fracture, liver dysfunction, and cytopenia occur as this is a severe form. In this type of main symptoms include weight loss, malabsorption, anemia, etc.
1.2.4) Mast Cell Leukemia (MCL): This type of systemic mastocytosis is rare but highly aggressive as mast cells are found in the blood and symptoms of this type include severe organ failure.
1.2.5) Mast Cell Sarcoma (MCS): This is a malignant tumor of mast cells that is rare but progresses rapidly and is often fatal.
2. Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS)
MCAS does not involve an increase in the number of mast cells but rather their abnormal activation of the mast cells, which leads to excessive release of inflammatory mediators in the body. It is further divided into three types:-
2.1) Primary MCAS: This type of MCAS mainly occurs due to KIT gene mutation i.e. gene mutation in mast cells which overlaps with indolent Systemic Mastocytosis.
2.2) Secondary MCAS: This type of MCAS is triggered by external factors such as allergens, infections, autoimmune diseases, or drugs and is commonly seen in chronic inflammatory conditions.
2.3) Idiopathic MCAS: Its cause is not known but individuals experience recurrent symptoms of abnormal mast cell activation without an increase in mast cell numbers.
In the above-mentioned types of MCAS, various symptoms are involved like gastrointestinal system symptoms like nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, etc. In the cardiovascular system symptoms like hypotension, dizziness, palpitation, etc. In the respiratory system symptoms like shortness of breath, wheezing, etc. In the skin symptoms like itching, hives, angioedema, and flushing, and along with this in the nervous system symptoms like headache, anxiety, and brain fog develop.
3) Other Mast Cell-Related Disorders
The conditions under this type are linked to mast cell dysfunction but do not fit into the above-mentioned type. It is of three types:
3.1) Hereditary Alpha Tryptasemia (HaT): When extra copies of the TPSAB1 gene are formed as a genetic disorder, tryptase levels elevate in the body and the symptoms appear like flushing, connective tissue issues, anaphylaxis, etc. which overlaps with MCAS.
3.2) Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES) with Mast Cell Activation: The rare condition in which mast cells and eosinophils are overactive and cause severe allergic reactions and even tissue damage.
3.3) Mast Cell Disorders in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) and POTS: Patients with hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (hEDS) and Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) experience mast cell activation symptoms.t, animal dander, extreme heat, extreme cold, mold, anxiety, chronic stress, etc.
Causes of Mast Cell Diseases
- KIT Gene Mutation i.e. KIT D816V mutation is the most common genetic cause of systemic mastocytosis which leads to uncontrolled mast cell proliferation.
- Hereditary Alpha Tryptasemia – HaT (TPSAB1 Gene Mutation) which increases tryptase levels, leading to mast cell overactivation.
- Due to familial Mast Cell Disorders
- Trigger causes due to allergens like Pollen, dust mites, animal dander, mold, etc.
- Intake of certain foods like nuts, shellfish, dairy products, etc.
- Viruses like Epstein-Barr virus, COVID-19, etc.
- Bacterial infection by Helicobacter pylori, etc.
- Lyme diseases
- Parasitic infections.
- Dysregulated immune responses
- Exposure to heat, cold, pressure, exercise, etc.
- Stress
- Intake of certain drugs like NSAIDs, opioids, beta-lactam antibiotics, etc.
- Use of contrast dyes.
- Use of histamine-releasing drugs.
- Hormonal Changes during pregnancy, menopause, menstruation, etc.
- Imbalance in gut microbiota (dysbiosis)
Causes of Mast Cell Diseases – As Per Ayurveda
- Tridosha vitiation i.e. Vata, Pitta, and Kapha
- Blood Tissue vitiation (Rakta Dhatu Dushti)
- Lymph and Plasma vitiation (Rasa Dhati Dushti)
- Muscle Tissue vitiation (Mamsa Dhatu Dushti)
- Blood channels vitiation (Rakta Vaha Srotas Dushti) (Blood Channels): Skin rashes, flushing, urticaria.
- Incompatible Diets (Viruddha Ahara) like mixing dairy with fish, sour with milk, or excessively spicy foods, cold potency food with hot potency food leads to toxin (Ama) formation.
- Intake of heavy food (Guru Bhojana)
- Frequent eating without digestion of previous meal (Adhyashana)
- Weak Digestive Fire (Manda Agni)
- Unhealthy Lifestyle (Mithya Vihara)
- Excessive exposure to cold (Sheeta), heat (Ushana), etc.
- Over-exertion (Ati-Vyayama)
- Daytime sleeping (Diwa Swapna)
- Over stress, fear (Bhaya), anxiety (Chinta), etc.
Symptoms of Mast Cell Diseases
Gastrointestinal Symptoms:-
- Bloating
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- GERD
- Peptic ulcers
- Food intolerance
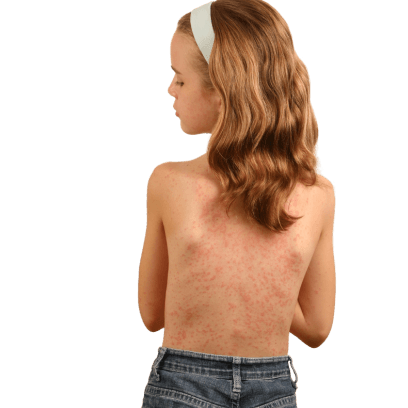
Dermatological Symptoms:-
- Sudden redness especially in the neck and face (Flushing)
- Angioedema
- Urticaria pigmentosa
- Visible small blood vessels on the skin (Telangiectasia)
Cardiovascular Symptoms:-
- Tachycardia
- Anaphylaxis
- Hypotension
- Fainting dizziness
Respiratory Symptoms:-
- Frequent nasal congestion
- Bronchospasm
- Wheezing
- Breathlessness
Musculoskeletal Symptoms:-
- Joint stiffness
- Joint pain
- Osteoporosis
Symptoms of Mast Cell Diseases – As Per Ayurveda
Based on the Dosha Imbalance
1. Vata Imbalance (Vata Prakopa):
- Dryness of skin (Sosha)
- Tremors (Kampana)
- Fatigue (Alpashakti)
2. Pitta Imbalance (Pitta Prakopa)
- Burning sensation (Daha)
- Acid reflux (Amloudgara)
- Heat intolerance (Ushana Asahishunta)
3. Kapha Imbalance (Kaphaja Prakopa)
- Itching (Kandu)
- Swelling (Shotha)
- Heaviness in the body (Guru Gatrata)
- Excess mucus production (Kapha Prasheka)
Based on Tissue (Dhatu) Involvement
Plasma and Lymph Impairment (Rasa Dhatu Dushti):
- Swelling (Shotha)
- Stiffness (Stambh)
- Itching (Kandu)
Based on Blood Impairment (Rasa Dhatu Dushti):
- Skin rashes, hives, etc. (Twaka Roga)
- Bleeding disorder (Rakta Pitta)
Based on Muscle and Connective Tissue Impairment (Mamsa Dhatu Dushti)
- Joint pain (Sandhi Shula)
- Muscle weakness (Mamsa Dourbalya)
Based on Nervous System Dysfunction (Majja Dhatu Dushti)
- Dizziness (Bhrama)
- Memory loss (Samriti Bhransha)
- Mental instability (Unmada)
What is the Role of KIT Genes in Mast Cells?
The KIT gene encodes the CD117 which is a tyrosine kinase receptor found on mast cells that binds to the Stem Cell Factor (SCF), a growth factor necessary for mast cell differentiation, activation, and survival. When mutation in KIT, especially in KIT D816V occurs, it leads to uncontrolled mast cell proliferation and mast cell survival, which results in mastocytosis. Even without SCF binding the mutated KIT receptor remains constantly activated, which results in excessive mast cells in tissues and Mast cell diseases occur as a result of this.
What is the Role of the TPSAB1 Gene in Mast Cells?
Mast cell granules store alpha- and beta-tryptase enzymes, which are encoded by the TPSAB1 gene. This type of enzyme is a key mediator in allergic responses, tissue remodeling, inflammation, etc. When a person has extra copies of TPSAB1 hereditary it leads to high tryptase levels which cause mast cell hyperreactivity, connective tissue abnormalities, etc.
Diagnosis of Mast Cell Diseases – As Per Ayurveda
Ayurvedic diagnosis of mast cell diseases is based on five diagnostic factors (Nidana Panchaka) and examination of Dosha, tissue (Dhatu), and Srotas involvement. Three-fold examination (Trividha Pariksha), and eightfold examination (Ashtavidha Pariksha) are also done to find out the underlying cause.
Along with this help of modern diagnostic tests are also taken like serum tryptase test, bone marrow biopsy, skin biopsy, pulmonary function test, CBC, etc. to detect high mast cell activity, to confirm mast cell infiltration, for diagnosis of chronic inflammation and eosinophilia, etc. Since symptoms of mast cell diseases vary from skin rashes and flushing to gastrointestinal disturbances, respiratory issues, neurological symptoms, etc., therefore mast cell diseases are often misdiagnosed. Proper identification and management through lifestyle adjustments, dietary modifications, and Ayurvedic interventions can help improve quality of life.

Have A Health Issue?
Consult Online
- Dr. Sahil Gupta (B.A.M.S., M.H.A.)
Ayurvedic Allergy Specialist
CEO & Founder of IAFA®
At last, Easier Mast Cell Diseases Management

Trusted by
More than 90,000 Patients

Convenient
at-Home Treatments

9.2 / 10
Customer Satisfaction Score
Ayurvedic Treatment for Mast Cell Diseases
We at IAFA Ayurveda provide safe and effective Ayurvedic Treatment for Mast Cell Diseases which includes herbs, detoxification therapies (Panchakarma), dietary and lifestyle modifications, etc.
These ayurvedic solutions relieve symptoms of mast cell diseases naturally and sets you free from mast cell diseases. The Ayurvedic approach that is used to treat mast cell diseases is as follows:-
Detoxification Therapy (Shodhana Therapy) for Mast Cell Diseases
1. Emetic Therapy (Vamana) – For expelling excessive Kapha-Pitta from patients of mast cell diseases, controlled therapeutic vomiting is done by using various herbs like Glycyrrhiza glabra (Madhuka), etc. It helps in conditions like histamine intolerance and chronic allergic reactions due to mass cell overactivation.
2. Purgation Therapy (Virechana) – Therapeutic purgation is also done in mass cell disease patients with the help of various herbs like Triphala, Aargwadha, etc. where over-mast cell activation has occurred.
3. Medicated Enema Therapy (Basti) – In this process, medicated oil or decoctions are administered through the rectum to balance Vata and Pitta which ultimately helps in controlling the inflammatory response. Tikta Ksheer Basti i.e. milk medicated with bitter herbs is very beneficial in this.
4. Bloodletting Therapy (Rakta Mokshana) – With the use of various techniques like leech therapy (Jalaukavacharana), the removal of impure blood is done from the body in bloodletting therapy. This procedure is very good for removing toxins from Rakta Dhatu in the body which is ultimately beneficial for symptoms like urticaria, angioedema, anaphylaxis, etc. in mast cell diseases.
5. Nasal Therapy / Intra Nasal Instillation (Nasya) – Medicated oil Shad Bindu Taila, Anu Taila, etc. is administered through the nostril which helps in preventing allergic responses.
Herbs for Mast Cell Diseases
Herbs for Mast Cell Disease Ayurvedic Treatment includes Haridra (Curcuma longa), Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera), Neem (Azadirachta indica), Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia), Shigru (Moringa oleifera), Shatavari (Asparagus racemosus), Mundi (Sapheranthus indicus), Kanchnaar (Bauhinia variegata), etc.
These herbs possess anti-inflammatory, mast cell stabilizer, immunomodulatory, natural histamine, antioxidant, etc. properties due to various active ingredients present in them like curcumin, quercetin, nimbidin, kaempferol, eugenol, etc. which makes them ideal drugs for treating mast cell diseases.
Gem Therapy for Mast Cell Diseases
Few stones are recommended to wear in mast cell diseases, as per Vedic Astrology. These stones can be worn after proper consultation with an astrologer as per your birth date, Zodiac sign, etc. to get only benefits.
As per astrology, Emerald (Panna), Moonstone (Chandrakant), and Blue Sapphire (Neelam) can be worn as per your natal chart if you are suffering from mast cell diseases. These stones help in reducing histamine overload, reducing Pitta, strengthening the immune system, and reducing stress-induced mast cell activation. tc.
Diet and Lifestyle Guidance (Pathya-Apathya) for Mast Cell Diseases
According to Ayurveda, if your diet is correct then medicine is of no use because a good gut is considered as the basis of a healthy individual. So, by giving attention to our daily diet, we not only get relief from the diseases from which we suffer but also avoid the upcoming diseases. Below we mention some dietary and lifestyle guidelines that one can follow for Mast cell diseases:-
What to Do (Pathya) in Mast Cell Diseases?
- Freshly prepared and easily digestible food (Laghu Aahara) should be taken.
- Intake of low histamine diet.
- Consume anti-inflammatory food like turmeric, ginger, etc.
- Drink plenty of water and stay hydrated.
- To prevent histamine surges, eat at regular intervals.
- Clarified butter (Ghrita) and coconut water should be included in the diet.
- For stress management practice Yoga, and meditation daily.
- Get plenty of sleep.
- Consume probiotic-rich food.
What to Avoid (Apathya) in Mast Cell Diseases?
- Avoid excessive spicy (Katu), sour (Amla), and salty (Lavana) food.
- Nightshade vegetables like eggplant, potato, etc. should be avoided.
- Histamine-rich food should be avoided like processed meat, alcohol, fermented food, aged cheese, etc.
- Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures i.e. too hot and too cold.
- Avoid the use of strong chemicals in cosmetics, perfumes, etc.
- Avoid irregular meal timing.
- Avoid fruit triggers like gluten and artificial additives.
- Avoid high-FODMAP diets.
Yoga Asanas for Mast Cell Diseases
Various Yoga Asanas like Tree pose (Vrikshasana), Cobra pose (Bhujangasana), Corpse pose (Shavasana), Reclined butterfly pose (Supta Baddha Konasana), Deep breathing technique (Pranayama) like Cooling breathes (Sheetali Pranayama), Humming bee breath (Bhramari Pranayama), Meditation, etc. can be used in mast cell diseases.
These Yogic Asanas calm histamine response, are helpful in skin rashes, and allergic reactions, and reduce anxiety. Along with this Trataka and chanting Om is also very beneficial in mast cell diseases.

Frequently Asked Questions
Question: How to Treat Mast Cell Disease Naturally?
Answer: By using various Ayurvedic herbs, detoxification therapy (Panchkarma), lifestyle modification, and stress management, one can treat mast cell diseases naturally as it helps to reduce inflammation and stabilize mast cells.
Question: What is the Most Powerful Natural Mast Cell Stabilizer?
Answer: Flavonoid quercetin is one of the best mast cell stabilizers. It is present in various Ayurvedic herbs like turmeric, Guduchi, Brahmi, Neem, etc.
Question: What Foods Reduce Mast Cells?
Answer: A diet is rich in anti-inflammatory foods i.e. Pitta pacifying diets like vegetables and fruits (Except histamine rich fruits and vegetables), fennel, coconut water, etc helps to regulate mast cells in the body.
Question: Is Turmeric Good for Mast Cells?
Answer: Yes, curcumin is present in turmeric which is an excellent anti-inflammatory and mast cell stabilizer that helps in reducing histamine from the body.
Question: How to Deactivate Mast Cells?
Answer: To deactivate mast cells naturally various cold potency herbs (Sheeta Virya Dravya), and detoxification therapies can be used. Along with this avoidance of allergens, processed food, etc. so helps in deactivating mast cells.
Question: Is Ginger Good for Mast Cells?
Answer: Yes, ginger has anti-inflammatory properties so it is good for mast cells but it should be taken in moderation as it is hot potency and it can aggravate Pitta. It is recommended to use it in combination with other cold-potency herbs (Sheeta Virya Dravya).
References
- Makhija, Inder & Shreedhara, Chandrashekara & H N, Aswatha. (2013). Mast cell stabilization potential of Sitopaladi churna: An ayurvedic formulation. Pharmacognosy research. 5. 306- 8. 10. 4103/ 0974- 8490. 118824.
- Zalawadia, Rishit & Gandhi, Chintan & Patel, Vaibhav & Balaraman, Ramachandran. (2009). The protective effect of Tinospora Cordifolia Linn. on various mast cell-mediated allergic reactions. Pharmaceutical Biology. 47. 1096-1106. 10. 3109/ 1388020- 090300- 8690.
- Mathew, Jessy & Srinivasan, K.K. & Dinakaran, Vachala & Joseph, Alex. (2009). Mast cell stabilizing effects of Sphaeranthus indicus. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 122. 394- 6. 10. 1016/ j. jep. 2009. 01. 015.
- Mali, Ravindra & Dhake, Avinash. (2011). Mast Cell Stabilizing Activity of Bauhinia variegata. Journal of Herbs. Spices & Medicinal Plants. 268- 274. 10. 1080/ 10496475. 2011. 602204.
- Ojha, Nisha. (2013). Critical Analysis of Charakokta Mahakashaya in the Management of Respiratory Allergic Disorders (RAD). Journal of Homeopathy & Ayurvedic Medicine. 02. 10. 4172/ 2167- 1206. 1000127.
- Ozdemir O, Kasımoglu G, Bak A, Sutluoglu H, Savasan S. Mast cell activation syndrome: An up-to-date review of the literature. World J Clin Pediatr. 2024 Jun 9; 13 (2): 92813. doi: 10. 5409/ wjcp. v13. i2. 92813. PMID: 38948000; PMCID: PMC- 11212760.
- Valent P, Akin C, Hartmann K, Alvarez-Twose I, Brockow K, Hermine O, Niedoszytko M, Schwaab J, Lyons JJ, Carter MC, Elberink HO, Butterfield JH, George TI, Greiner G, Ustun C, Bonadonna P, Sotlar K, Nilsson G, Jawhar M, Siebenhaar F, Broesby-Olsen S, Yavuz S, Zanotti R, Lange M, Nedoszytko B, Hoermann G, Castells M, Radia DH, Muñoz-Gonzalez JI, Sperr WR, Triggiani M, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Galli SJ, Schwartz LB, Reiter A, Orfao A, Gotlib J, Arock M, Horny HP, Metcalfe DD. Updated Diagnostic Criteria and Classification of Mast Cell Disorders: A Consensus Proposal. Hemisphere. 2021 Oct 13; 5 (11): e646. doi: 10. 1097/ HS9. 000000- 000000- 0646. PMID: 3490- 1755; PMCID: PMC- 8659997.
- Jennings SV, Finnerty CC, Hobart JS, Martín-Martínez M, Sinclair KA, Slee VM, Agopian J, Akin C, Álvarez-Twose I, Bonadonna P, Bowman AS, Brockow K, Bumbea H, de Haro C, Fok JS, Hartmann K, Hegmann N, Hermine O, Kalisiak M, Katelaris CH, Kurz J, Marcis P, Mayne D, Mendoza D, Moussy A, Mudretzkyj G, Vaia NN, Niedoszytko M, Elberink HO, Orfao A, Radia DH, Rosenmeier S, Ribada E, Schinhofen W, Schwaab J, Siebenhaar F, Triggiani M, Tripodo G, Velazquez R, Wielink Y, Wimazal F, Yigit T, Zubrinich C, Valent P. Mast Cell Diseases in Practice and Research: Issues and Perspectives Raised by Patients and Their Recommendations to the Scientific Community and Beyond. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022 Aug;10 (8): 2039- 2051. doi: 10. 1016/ j. jaip. 2022. 06. 018. Epub 2022 Jun 28. PMID: 3577- 7651.
- Baran J, Sobiepanek A, Mazurkiewicz-Pisarek A, Rogalska M, Gryciuk A, Kuryk L, Abraham SN, Staniszewska M. Mast Cells as a Target-A Comprehensive Review of Recent Therapeutic Approaches. Cells. 2023 Apr 19; 12 (8): 1187. doi: 10. 3390/ cells- 12081187. PMID: 37190096; PMCID: PMC- 10136699.
Seeking Expert Advice
IAFA Ayurveda helps in pacifying aggravated Dosha, balancing the Dhatu and Strotas Dushti, and strengthening the immunity. With a root-cause approach, experience long-term relief and improved well-being in mast cell diseases.
Book Your Consultation Today for A Natural, Side-Effect-Free Ayurvedic Solution to Mast Cell Diseases at IAFA!
Was this Page Helpful?
So, IAFA’s Root-Cause Treatment for Mast Cell Diseases is Just 3 Steps Away!

01. Connect With Us
Share your history of illness or Book your appointment

02. Consult With Us
Dr. Gupta a certified Ayurvedic Allergist Consultant

03. Root Cause Treatment
Get an accurate diagnosis, medicines, diet & lifestyle change
Real Case Studies – Successfully Treated Patients
Real Case Studies of Successfully Treated Patients from All Around the World by IAFA Ayurveda®

9 Year Old Female Patient Recovered from Chronic Allergic Bronchitis – A Case Study
This case study presents a 9-year-old female patient who has successfully recovered…

12-Year-Old Child Recovered from Sun Allergy and Polymorphous Light Eruption (PMLE) – A Case Study
This is a case study of a 12-year-old child who has successfully…

40-Year-Old Female Patient Recovered from Dyshidrotic Eczema and Onychomycosis – A Case Study
This case study highlights the successful recovery of a 40-year-old female patient…

40-Year-Old Female Patient Recovered from Urticaria and Angioedema – A Case Study
This case study focuses on a 40-year-old female patient who has successfully…
Read More Articles

Mast Cell Diseases
Discover Ayurvedic treatment for Mast Cell Diseases, including types, causes, symptoms, and…

High Immunoglobulin-E (IgE) Levels
Discover Ayurvedic treatment for high Immunoglobulin-E (IgE) levels. Learn about the causes,…

Histamine Intolerance
Discover Ayurvedic treatment for histamine intolerance, its causes, symptoms, and natural treatment.…